Macrophages: the macrophage response following phagocytosis of apoptotic cells
Emeritus professor of TOHO UNIVERSITY.
|
Macrophages: the macrophage response following phagocytosis of apoptotic cells |
|
Kobayashi,Yoshiro, Emeritus professor of TOHO UNIVERSITY. |
A large number of cells die every day in our body through apoptosis. In this homepage, I would like to introduce our recent study on the macrophage response following or during phagocytosis of apoptotic cells.
![]() What is apoptosis?
What is apoptosis?![]() Difference between apoptotic cells and live cells
Difference between apoptotic cells and live cells ![]() Our research
Our research
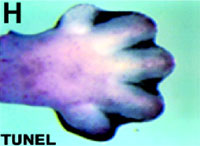
One of the most famous examples of apoptosis is bud formation during which many interdigital cells die. They are stained black by a TUNEL method*, as shown in the figure left. They are then cleared up by neighboring phagocytes to form fingers.
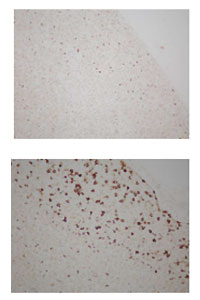
The other famous example is seen in the thymus. Many thymocytes are subject to negative selection, undergoing apoptosis, as shown in the upper figure left. In the lower figure, much more apoptotic cells are detected in the thymus from an X-irradiated mouse. Here they are stained brown with anti-ss (single stranded) DNA antibodies. These pictures were obtained by an undergraduate student in 2004 (AS; the names of students are hereafter indicated by their initials). The dead cells are then cleared up by thymic macrophages.
Thus apoptosis occurs even in a normal body. Then what happens in macrophages upon phagocytosis of dead cells? Apoptotic cell clearance proceeds silently without inflammation. In contrast, necrotic cells are often associated with inflammation, because it has been believed that cytosolic constituents such as proteins are leaked out from necrotic cells but not apoptotic cells and that some of them induce inflammation (Science 267, 1445-62, 1995). These include HMGB1 (High Mobility Group B1) scollectively called DAMPs (Damage Associated Molecular Pattern Molecules). Inflammation is a localized reaction upon infection, for instance, and is associated with infiltration of white blood cells, an increase in permeability of blood vessels and enlargement of blood vessels, causing redness, fever, pain and swelling.
Mature dendritic cells are very important in initiating an immune response. When dendritic cells are immature, they can also clear up dead cells. Then what happens in immature dendritic cells upon phagocytosis of dead cells? Immature dendritic cells do not mature after phagocytosis of apoptotic cells, whereas they do after phagocytosis of necrotic cells to present antigens to T cells (Nature Medicine 5, 1249-55, 1999). This is how immature dendritic cells do not present antigens to auto-reactive T cells even after phagocytosis of many apoptotic cells occurring in our body.
![]()
BACK / HOME(English) / NEXT